The Role of Dual-Use Solar Panels in Agriculture
____________________________________________________________________________
By: Jane Marsh
The agricultural industry is adopting solar technologies to support sustainability trends. Farmers can remain competitive in the industry by meeting eco-consumer demands. They may also reduce their production costs by using independent energy supplies.
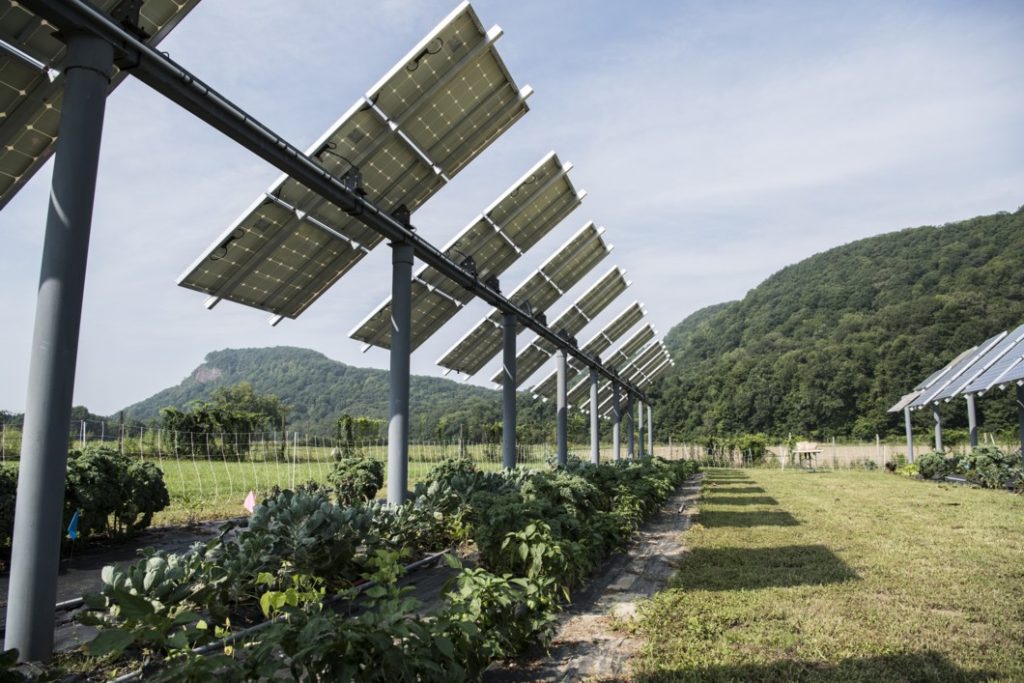
Agricultural professionals can rely on dual-use solar panels to improve crop yields and cost-efficiencies. The technology also minimizes emissions, which supports environmental conservation and protects farmers’ health. Individuals may adopt photovoltaic (PV) solar panels to enhance the sustainability of crop production.
The Demand for Dual-Use Farm Panels
More farmers are investing in PV panels to meet their financial needs. Agricultural property taxes across America increased by two billion dollars between 2012 and 2017. Many local, family-owned farms went out of business as property taxes increased.
Small-scale farmers are installing PV panels to reduce utility costs and create a passive form of income. Farmers can sell excess electricity back to their local grids and fund a portion of their property costs. Another demand for dual-use solar comes from environmental conditions.
Farmers in arid regions struggle to maintain sufficient crop yields because of soil erosion. Earth’s rising temperature increase the global evaporation rate. Dehydrated soil has fewer nutrients compared to its natural state.
Agricultural professionals can improve crop yields and minimize operational limitations using dual-use solar panels. They may support their PV panel costs using the solar investment tax credit (ITC). Tax credits can help farmers pay off their initial panel costs and installation fees.
Growing Low-Light Crops
Farmers are improving their crop production and financial stability using dual-use PV panels. One benefit of using panels is to support low-light plant growth. Farmers struggle to produce low-light plants as Earth’s temperature rises and environmental conditions shift.
Individuals may support crop development by placing low-light plants beneath PV panels. The panels keep crops cool and minimize ultraviolet (UV) light damage. Farmers can optimize their outputs by utilizing PV panels for crop production.
PV-Powered Water Pumps
Grain is one of the most common crops and it requires consistent moisture. The crops also require adequate soil quality. PV panels can power water pumps to keep crops moist and prevent soil erosion.
Solar water pumps rely on PV arrays, electric motors and conventional pumps. The technology either uses direct or alternating currents to power electric motors. Farmers can decrease watering costs by using independent energy supplies.
They can optimize crop watering practices by investing in the most effective pumps. There are two common variations of solar water pumps. The submersible pump resides below the ground level and uses solar power to move water up from a well.
Surface pumps use renewable energy to pump groundwater into an overhead tank. The tank can distribute freshwater to automated sprinkler systems. Investing in the most compatible solar water pumps can minimize field operation costs and reduce resource exploitation.
Selling Solar Power to the Grid
Farmers can also use PV panels to combat rising operation costs. They may sell solar power to local electricity grids for a profit. Agricultural professionals can invest in advanced electricity storage systems to reduce energy waste and improve profits.
Individuals may install hydrogen storage tanks on their farms to hold excess electricity. The systems rely on electrolyzers to convert solar power into hydrogen for prolonged storage. Farmers can produce more electricity to sell using renewable energy storage technologies.
Producing solar power on farms also increases revenue by attracting eco-consumers.
Environmentalists make up a significant portion of the eco-consumer market. Researchers found about 85% of consumers will pay higher costs for sustainable goods and services. Producing crops with emission-free electricity helps farmers meet eco-consumer demands and improve their profitability.
Agricultural Solar Technologies on the Horizon
Environmental engineers are advancing solar technologies to improve the agricultural industry’s sustainability. They are developing floating PV panels, which farmers may use to optimize their water sources and produce electricity. Placing floating panels on canals and rivers reduces water loss from evaporation.
Engineers are also creating solar noise barriers, which farmers may use to protect their animals from disorienting external features. The walls generate emission-free electricity while optimizing grazing conditions. Farmers in urban environments can place the barriers around their grazing land to minimize livestock production disruptions.
Developing Sustainable Agricultural Environments
The built environment consumes a significant portion of Earth’s surface. Individuals can optimize agricultural development to meet global dietary needs by optimizing land conservation. Developers may install more PV panels on farms to create dual uses for undeveloped land.
They can install solar panels in fields and on rooftops to improve clean-electricity production rates. Developing sustainable agricultural environments protects local ecosystems and farmers’ health and well-being. Reducing energy-related emissions improves farmers’ and livestock’s lung health.
Author bio:
Jane works as an environmental and energy writer. She is also the founder and editor-in-chief of Environment.co.