Covid-19 recovery and fossil fuels – A time for change
OECD – Paris, 5 June 2020
As governments design stimulus measures for economies hit by the Covid-19 crisis, they should seize the opportunity of historically low oil prices to redirect some of the half a trillion dollars spent annually supporting fossil fuels into sustainable investment including low-carbon energy, according to the OECD and the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Government support for the production and consumption of fossil fuels totalled USD 478 billion in 2019, according to an analysis of 77 economies by the OECD and the IEA. While that marks an overall decline from 2018 as lower oil prices meant governments spent less subsidizing energy costs for end-users, the data also show a 38% rise in direct and indirect support for the production of fossil fuels across 44 advanced and emerging economies.
“I am saddened to see some backsliding on efforts to phase out fossil fuel support. This rise in production subsidies seems set to continue in 2020 with some countries targeting state aid to fossil fuel and related industries,” said OECD Secretary-General Angel Gurría. “Subsidising fossil fuels is an inefficient use of public money and serves to worsen greenhouse emissions and air pollution. While our foremost concern today must be to support economies and societies through the Covid-19 crisis, we should seize this opportunity to reform subsidies and use public funds in a way that best benefits people and the planet.”
G20 countries pledged in 2009 to gradually phase out inefficient fossil fuel subsidies. As well as encouraging consumption, fossil fuel subsidies are an ineffective way to support low-income households compared to targeted benefits and tend to favour wealthier households that use more fuel and energy. Money spent supporting coal, oil and gas could instead be invested in sustainable energy infrastructure, research and job training. In the Covid-19 climate, subsidies drain resources that could be spent on strengthening health system preparedness and resilience, for example.
The combined OECD-IEA estimate of fossil fuel support in 2019 shows an 18% decline from USD 582 billion in 2018 that is due mostly to the mechanical effect of the drop in global oil prices on consumption subsidies. On the production side, while several countries reduced support for coal production and state aid to coal-fired power plants, others increased support to oil and natural gas industries, mostly through investments in infrastructure, budgetary support to absorb corporate debt or preferential tax treatment for spending on production.
The OECD’s analysis of budgetary transfers, tax breaks and spending programmes linked to the production and use of coal, oil, gas and other petroleum products in 44 OECD and G20 countries showed total fossil fuel support rose by 10% to USD 178 billion in 2019, ending a five-year downward trend. (See the OECD Inventory of Support Measures for Fossil Fuels and a data visualisation with support by fuel, economic sector and indicator.)
IEA analysis of government interventions that keep end-user prices artificially low in 42 economies finds that consumption subsidies dropped by USD 120 billion in 2019, largely due to lower market prices. The further plunge in oil prices this year offers a clear chance to wean economies off this support. (See IEA key findings on energy consumption subsidies.)
“Fossil fuel subsidies are a roadblock to achieving a sustainable recovery from the Covid-19 crisis,” said Dr Fatih Birol, Executive Director of the IEA. “Today’s low fossil fuel prices offer countries a golden opportunity to phase out consumption subsidies. As governments look to boost jobs and plan for a better and more resilient future, it is essential to avoid market distortions that favour polluting and inefficient technologies.”
The IEA predicts that the plunge in fossil fuel prices and use catalysed by Covid-19 is set to bring down consumption subsidies to USD 180 billion in 2020, which would be the lowest level since it began tracking the data in 2007. Meanwhile, sharp declines in revenues from oil and gas production make subsidy reforms crucial to ease pressure on public finances in producer economies. (Read more.)
Source: OECD

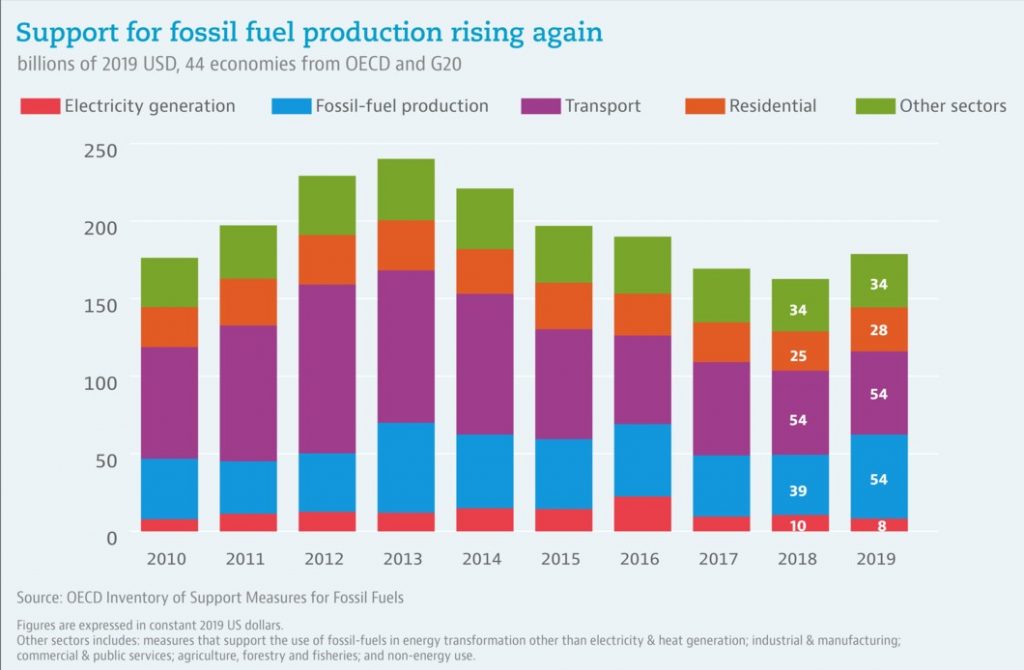 Source: OECD
Source: OECD




